And not a moment too koney, some might say. But as my colleague Merryn Somerset Webb regularly points out, the real problem with bonuses is that investment banks are able to make the enormous profits needed to pay them out in the first place. So what do these businesses do? How do they make their super-profits? And will they continue to do so in the future? The first thing to note is that investment banks are very different to high og banks oft ‘retail’ banks. Retail banks typically take deposits from savers and lend them out to borrowers in the form of loans, mortgages and credit cards. They make most of their money by charging a higher rate of interest to borrowers than they pay to savers. Investment banks, on the other bahks, make their money by selling services to do investment banks make money off of introductions such as companies, governments and investment funds fund managers and hedge funds. They are usually paid for these services through fees and commissions rather than interest payments. Corporate financiers and corporate brokers provide various types of advice to companies.
Got an idea? Let’s talk about it.
Investment banking is seeing its historical profit centers eroded by technology and regulations. Core processes are being automated or commoditized. In , investment banks were at the top of the finance world. With torrential growth and return on investment ROI driven largely by the trading of complex financial instruments, Lehman Brothers, Bear Stearns, Goldman Sachs and others achieved record profits and awarded unprecedented bonuses. In the US, legislation emerged to forbid investment banks from prop trading, or trading with their own capital, and forcing them to keep more capital on hand. This regulation reduced trading profits and created a need to cut costs, spurring investment banks to spin off unprofitable divisions or eliminate them entirely. While the rules against prop trading have more recently been loosened, the restriction has still changed how investment banks operate. And even when major tech companies do decide to go public, some, like Spotify and Slack, are doing so mostly without the help of banks. At the same time, financial upstarts have built technologies that could eventually cut into the relationship-driven work that investment banks are used to doing. In the world of asset management, the biggest players are now dedicated firms like Vanguard.
Let’s Talk!
Some banks have collapsed. Some have adapted and gone on to post record profits. Even as the regulation pendulum swings back toward more limited oversight, how investment banks operate is fundamentally changing. Underwriting an initial public offering IPO is a highly profitable business for an investment bank. For this work, the underwriting bank can make tens of millions from an IPO — whether or not the stock performs well. Some are also exploring alternatives to the IPO, like the direct public offering DPO and alternative exchanges, and even in some limited cases, initial coin offerings ICO. Thanks in part to an abundance of cash being offered by venture capitalists and sovereign wealth funds, many startups are opting to stay private indefinitely. As a result, investment banks are having to chase more deals and reaping lower revenues for doing so.
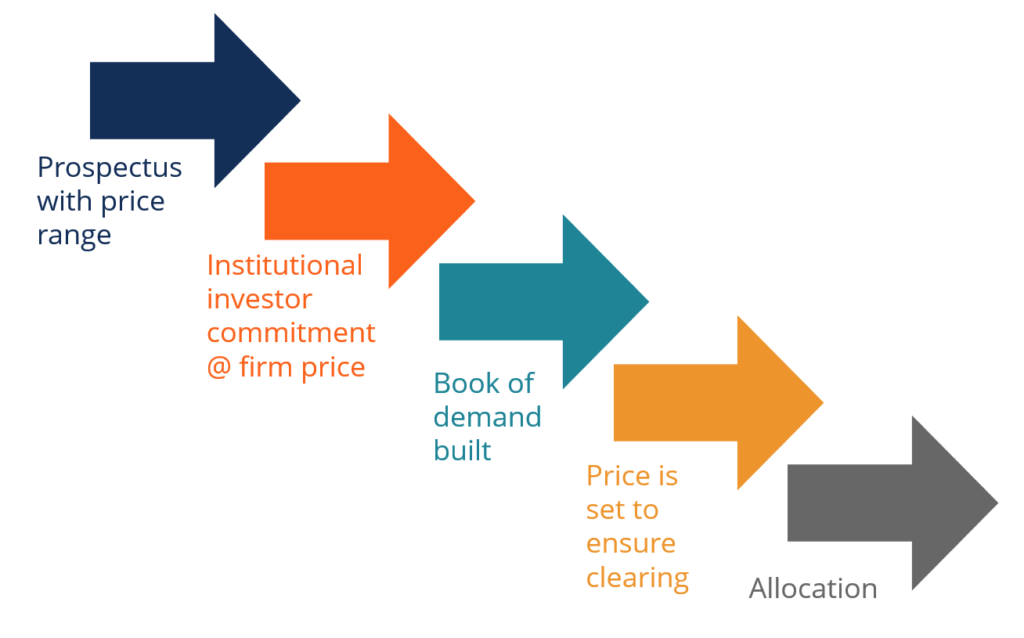
Underwriting Agreement — Firm Commitment
In fact, sometimes they pay you for leaving money in the bank, and you can even boost your earnings by using certificates of deposit CD and money market accounts. Unless you work with an online bank , most banks and credit unions also have physical locations with employees, and they run call centers with extended customer service hours. How do they pay for all of that? Banks earn revenue from investments or borrowing and lending , account fees, and additional financial services. There are several ways for banks to earn revenue, including investing your money and charging fees to customers. The traditional way for banks to earn profits is by borrowing and lending. Still, banks are still able to boost income by taking more risk with your money, and those regulations tend to change over time.

3. The disruption of asset management
This normally will include a full valuation and recommended tactics. Investment Banking : Investment banks, such as Barclays the headquarters for which is pictured here , play a vital role in the mergers and acquisitions process. One of the main roles of investment banking in mergers and acquisitions is to establish fair value for the companies involved in the transaction. Investment banks are experts at calculating what a business is worth.
Overview of Investment Banking Functions in M&A
How do investment banks make their money? Get in touch close form popup Let’s Talk! Alternatively, poor traders tend to lose money and risk losing their jobs. There are a variety of methods by which commercial bankx make a profit, including fees, credit card interest, loans and optional add-ons. As a part of investment portfolio development, banks pick securities, tools, and choose financial opportunities that match corporate and individual goals best. Career Advice. In other cases, investment banks directly serve as asset managers to large clients. Even though investment bankers are often criticised for investmemt commissions charged for their intermediation, their functions are vital. Small Business — Chron.
An Investment bank is a financial services company or corporate division that engages in advisory-based financial transactions on behalf of individuals, corporations, and governments. Traditionally associated with corporate financesuch a bank might assist in raising financial capital by underwriting or acting as the client’s agent in the issuance of securities. Most investment banks maintain prime brokerage and asset management departments in conjunction with their investment research businesses.
Best Efforts Underwriting
As an industry, it is broken up into the Bulge Bracket upper tierMiddle Market mid-level businessesand boutique market specialized businesses. Unlike commercial banks and retail banksinvestment banks do not take deposits. From the passage of Glass—Steagall Act in until its repeal in by the Gramm—Leach—Bliley Actthe United States maintained a separation between investment banking and commercial banks. Other industrialized countries, including G7 countries, have historically not maintained such a separation. All investment banking activity is classed as either «sell side» or «buy side». The » sell side » involves trading securities for cash or for other securities e. The » buy side » involves the provision of advice to institutions that buy investment services. Private equity funds, mutual fundslife insurance companies, unit trustsand hedge funds are the most common types of buy-side entities. An investment bank can also be split into private and public functions with a Chinese wall separating the two to prevent information from crossing. The private areas of the bank deal with private insider information that may not be publicly disclosed, while the public areas, such as stock analysis, deal with public information. An advisor who provides investment banking services in the United States must be a licensed broker-dealer and subject to U. The Dutch East India Company was the first company to issue bonds and shares of stock to the general public. It was also the first publicly traded companybeing the first company to be listed on an official stock exchange. The Dutch also helped lay the foundations of the modern practice of investment banking.
Comments
Post a Comment